
Its Christmas time, and that means its time for another month of the always fantastic Festive Tech Calendar. This was one of the first events that I participated in when I was trying to break into blogging and public speaking and I’m delighted to be involved again this year.
This year, the team are raising funds for Beatson Cancer Charity who raise funds to transform the way cancer care is funded and delivered by funding specialists, research and education to invest in a better future for cancer patients. You can make donations via the Just Giving page.
In this post, I’ll walk through the extensive list of Container hosting options that are available on Azure. I’ll take a look at the Azure-native offerings, include some third-party platforms that run on Azure, and then compare them on performance, scalability, costs, and service limits.
What counts as “Container Hosting” on Azure?
For this post I’m treating a “container hosting option” as:
A service where you can run your own Docker images as workloads, with Azure (or a partner) running the infrastructure.
There are an extensive list of options (and I will exclude a few off the list below, but the main “go-to” options that I’ve seen in architecture discussions are:
- Azure Container Apps
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Azure Container Instances (ACI)
- Azure App Service (Web Apps for Containers)
- Azure Service Fabric (with containers)
- Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO) – OpenShift on Azure
- Kubernetes platforms on Azure VMs or Azure VMware Solution (VMware Tanzu, Rancher, etc.)
But what about the humble reliable Virtual Machine?

OK yes, its still out there as an option – the Virtual Machine with Docker installed to run containers. And its the place where most of us have started on this journey (you can check out a blog series I wrote a few years ago here on the subject of getting started with running Docker on VM’s).
There are still some situations where you will see a need for Virtual Machines to run containers, but as we’ll see in the options below, this has been superseded by the range of offerings available on Azure who can run containers from single instances right up to enterprise level offerings.
Azure Container Instances (ACI)
Lets start with the smallest available form of hosting which is Azure Container Instances. ACI is the “run a container right now without VMs or an orchestrator” service – there are no virtual machines or orchestrators to manage, and containers start within seconds on Azure’s infrastructure. ACI provides a single container or small group of containers (called a container group) on-demand. This simplicity makes it essentially “containers-as-a-service”.
You can run a container by issuing a single Azure CLI command. It’s completely managed by Azure: patching, underlying host OS, and other maintenance are invisible to the user. ACI also supports both Linux and Windows containers.
Its great for short-lived tasks and simple container groups, good examples of this would be Cron-style jobs, build workers, data processing pipelines, and dev/test experiments where you just want a container to run for a bit and then disappear.
Azure App Service (Web Apps for Containers)
Azure App Service (Web App for Containers) is a Platform-as-a-Service offering that lets you deploy web applications or APIs packaged as Docker containers, without managing the underlying servers.
This uses all of the features that you would normally see with App Service – you get deployment slots, auto-scaling, traffic routing, and integrated monitoring with Azure Monitor. The benefit of this is that it abstracts away the container management and focuses on developer productivity for web applications.
The use case of using App Service is the familiarity with the product. Its gives you predictable, reserved capacity and can be used to host HTTP APIs or websites where you don’t want to have the overhead of using Kubernetes, but want to utilise features like deployment slots, built-in auth, easy custom domains, built-in backup & integration.
Azure Container Apps
Azure Container Apps is a fully managed container execution environment, designed specifically for microservices, APIs, and event-driven processing.
It abstracts away the Kubernetes infrastructure and provides a serverless experience for running containers – meaning you can run many containers that automatically scale in response to demand and even scale down to zero when idle.
Container Apps sits on top of Kubernetes (it runs on Azure’s internal K8s with open technologies like KEDA, Dapr, and Envoy) but as a developer you do not directly interact with Kubernetes objects. Instead, you define Container Apps and Azure handles placement, scaling, and routing.
Container Apps is an ideal place for running Microservices, APIs and event-driven jobs where you don’t want to manage Kubernetes, and want to scale-to-zero and only pay when there’s traffic. Its a nice “middle ground” between App Service and full AKS.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
We’re finally getting to the good stuff!!
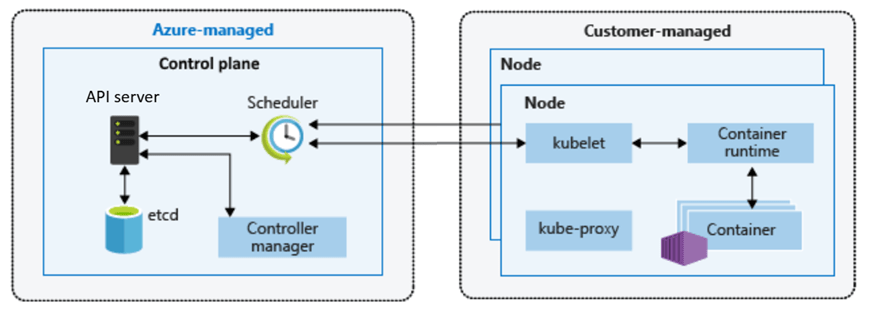
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is Azure’s flagship container orchestration service, offering a fully managed Kubernetes cluster.
With AKS, you get the standard open-source Kubernetes experience (API, kubectl, and all) without having to run your own Kubernetes control plane – Azure manages the K8s master nodes (API servers, etc.) as a service.
You do manage the worker nodes (agent nodes) in terms of deciding their VM sizes, how many, and when to scale (though Azure can automate scaling).
In terms of ease-of-use, AKS has a steep learning curve if you’re new to containers, because Kubernetes itself is a complex system. Provisioning a cluster is quite easy (via Azure CLI or portal), but operating an AKS cluster effectively requires knowledge of Kubernetes concepts (pods, services, deployments, ingress controllers, config maps, etc.).
It’s less turn-key than the earlier services – you are stepping into the world of container orchestration with maximum flexibility. One of the main benefits of AKS is that it’s not an opinionated PaaS – it’s Kubernetes, so you can run any containerized workload with any configuration that Kubernetes allows.
Another reason for choosing AKS is that you can run it locally in your environment on an Azure Local cluster managed by Azure Arc.
The main reason for choosing AKS is running enterprise or large-scale workloads that need:
- Full Kubernetes API control
- Custom controllers, CRDs, service meshes, operators
- Multi-tenant clusters or complex networking
If you’re already familiar with Kubernetes, this is usually the default choice.
Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO)
Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO) is a jointly managed offering by Microsoft and Red Hat that provides a fully managed OpenShift cluster on Azure.
OpenShift is Red Hat’s enterprise Kubernetes distribution that comes with additional tools and an opinionated setup (built on Kubernetes but including components for developers and operations). With ARO, Azure handles provisioning the OpenShift cluster (masters and workers) and critical management tasks, while Red Hat’s tooling is layered on top.
It’s a first-class Azure service, but under the covers, it’s Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. In terms of ease-of-use: for teams already familiar with OpenShift, this is much easier than running OpenShift manually on Azure VMs. The service is managed, so tasks like patching the underlying OS, upgrading OpenShift versions, etc., are handled in coordination with Red Hat.
The use case for ARO comes down to whether you’re an OpenShift customer already, or need OpenShift’s enterprise features (built-in pipelines, operators, advanced multi-tenancy).
Azure Service Fabric
Service Fabric predates AKS and was Azure’s first container orchestrator. I’ve not seen this ever out in the wild but it deserves a mention here as its still available as a container hosting platform on Azure.
Its a mature distributed systems platform from Microsoft, used internally for many Azure services (e.g., SQL DB, Event Hubs). It can orchestrate containers as well as traditional processes (called “guest executables”) and also supports a unique microservices programming model with stateful services and actors where high-throughput is required.
I’m not going to dive too deep into this topic, but the use case for this really is if you already have significant investment in Service Fabric APIs.
Third-party Kubernetes & container platforms on Azure
Beyond the native services above, you can also run a variety of third-party platforms on Azure:
- Kubernetes distributions on Azure VMs: VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid, Rancher, Canonical Kubernetes, etc., deployed directly onto Azure VMs.
- Azure VMware Solution + Tanzu: run vSphere with Tanzu or Tanzu Kubernetes Grid on Azure VMware Solution (AVS) and integrate with Azure native services.
There are a number of reasons for ignoring the native Azure services and going for a “self-managed” model:
- If you need a feature that AKS/ARO doesn’t provide (e.g., custom Kubernetes version or different orchestrator, or multi-cloud control plane).
- If you want to avoid cloud vendor lock-in at the orchestration layer (some companies choose BYO Kubernetes to not depend on AKS specifics).
- If your organization already invested in those tools (e.g., they use Rancher to manage clusters across AWS, on-prem and also want to include Azure).
- If you have an on-prem extension scenario: e.g., using VMware Tanzu in private cloud and replicating environment in Azure via AVS to have consistency and easy migration of workloads.
- Or if you require extreme custom control: e.g., specialized network plugins or kernel settings that AKS might not allow.
Comparison Summary
Lets take a quick comparison summary where you can see at a glance the ease of use, hosting, cost model and use cases of each service:
| Option | Ease of Use | Hosting Model | Cost Model | Best For |
| Azure Container Instances | Very High | Serverless | Pay per second of CPU/Memory, no idle cost. | Quick tasks, burst workloads, dev/test, simple APIs. |
| Azure App Service | High | PaaS | Fixed cost per VM instance (scaled-out). Always-on cost (one or more instances). | Web apps & APIs needing zero cluster mgmt, CI/CD integration, and auto-scaling. |
| Azure Container Apps | Moderate | Serverless | Pay for resources per execution (consumption model) + optional reserved capacity. Idle = zero cost. | Microservice architectures, event-driven processing, varying workloads where automatic scale and cost-efficiency are key. |
| Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | Low (for beginners). Moderate (for K8s proficient teams). | Managed Kubernetes (IaaS+PaaS mix) | Pay for VMs (nodes) only. Control plane free (standard tier) | Complex, large, or custom container deployments |
| Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO) | Moderate/Low – easy for OpenShift experts, but more complex than AKS for pure K8s users. | Managed OpenShift (enterprise K8s) | Pay for VMs + Red Hat surcharge. Higher baseline cost than AKS. | Organizations requiring OpenShift’s features (built-in CI, catalog, stricter multi-tenancy) or who have OpenShift on-prem and want cloud parity. |
| Azure Service Fabric | Low – steep learning curve | IaaS (user-managed VMs) with PaaS runtime | Pay for VMs No automatic scaling – you manage cluster size. | Stateful, low-latency microservices, or mixed workloads (containers + processes). Teams already leveraging SF’s unique capabilities. |
Conclusion
As we can see above, Azure offers a rich spectrum of container hosting options.
Serverless and PaaS options cover most workloads with minimal ops overhead, while managed Kubernetes and third-party platforms unlock maximum flexibility at higher complexity.
In my own opinion, the best way to go is to make the decision based on business needs and the core knowledge that exists within your team. Use managed and/or serverless options by default; move to Kubernetes only when needed.
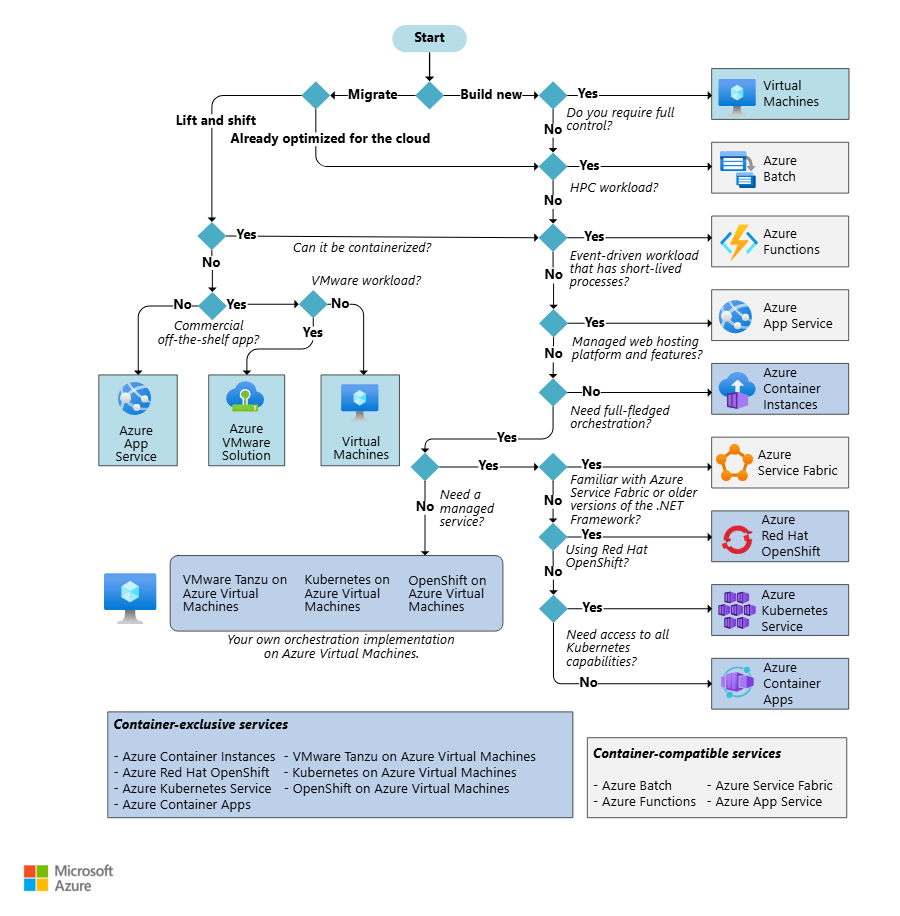
You can use the decision tree shown below as an easy reference to make the decision based on the workload you wish to run.
I hope this blog post was useful! For a deeper dive, you can find the official Microsoft guide for choosing a Container hosting service at this link.





